Floating Exchange Rate: Definition and How It Works
By Wilbert S
January 10, 2024 • Fact checked by Dumb Little Man
Want to jump straight to the answer? The best forex broker for traders is Avatrade
The #1 Forex Trading Course is Asia Forex Mentor
There are about 180 national currencies recognized by the United Nations (UN) in the world today. Each currency is issued and regulated by its central bank which may be independent or owned by the government. These central banks formulate monetary policies, fix interest rates, control the money supply, and perform other important duties. In most developing countries, the central banks maintain foreign reserves in U.S dollars (USD) or other strong currencies.
In this article, we will explain the meaning of a floating exchange rate system against fixed exchange rate regimes. We will go into the details of how the system works, why it is different, and how it came about. The review will end with the best forex trading course which is the ‘one core program’. Also, we’ve got Ezekiel Chew; the forex industry expert, corporate trainer, and successful trader, to share his take on Floating Exchange Rates.
What is Floating Exchange Rate?
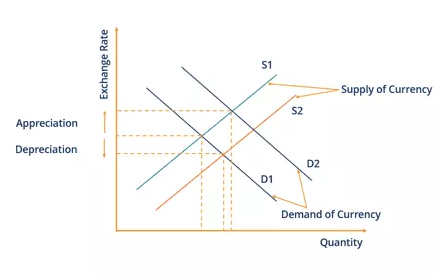
The term Floating exchange rate refers to a monetary policy where the exchange rates of a country’s currency are determined by the forex market forces of demand and supply. In this case, the currency is referred to as a ‘floating currency’. The exchange rates of floating currencies are affected by forex market events like the news, and economic releases such as interest rate percentages, unemployment rates, inflation figures, etc.
In a fixed exchange rate system, the government or central bank decides the exchange rates for its national currency. It is also known as ‘pegged exchange rate’ because it is usually pegged against the value of another currency, a commodity such as Gold, or a basket of selected currencies. Though it has the advantage of curbing large fluctuations and stabilizing the exchange rates; it comes with several complications.
Most of the nations in our world today use floating exchange rate regimes; only many still use fixed exchange rates regime. All the major currencies like U.S Dollar, Euro, Japanese Yen, etc use floating exchange rates. Even with the floating exchange rate systems in place, central banks and governments, especially in developing economies, still intervene in the foreign exchange market to protect their currency from devaluation.
How Floating Exchange Rates System Work

Floating exchange rate systems actually reflect the strength of a currency since its value is determined by the supply and demand of forex. The floating rate of a currency is subject to the political, economic, and social conditions of the nation that owns the currency. Countries that frequently experience disasters, high demand for foreign currency, inflation, unemployment, etc will experience frequent fluctuations in exchange rates.
In countries where there are high demands for foreign exchange; probably for importation or speculations, the local currencies suffer short-term fluctuations and decline in value. This is in line with the law of supply and demand which stipulates that prices go up when demand is greater than the supply but prices decline when supply is more than the demand. When the relative value of a local currency is appreciating, it encourages exports which helps in stimulating the economy.
Central banks always monitor their exchange rates and may occasionally intervene in the forex market when necessary; even in a free-floating exchange rate regime. When their local currency experience extreme fluctuations, a central bank must take action to protect it from further decline. These include adjusting interest rates, buying large quantities of foreign exchange with local reserves, etc.
What makes Fixed Exchange Rate Different?
A fixed exchange rate is when the government pegs its currency’s price against the value of another currency like the U.S dollar or a set of other currencies. This makes the exchange rate more stable as it is unaffected by forex market pressures. A hard peg is when the pegged rate is rigid and not easily changed while an adjustable peg is frequently changed by the government or central bank.
A fixed exchange rate system may be used to control inflation but this depends on the currency of reference. When the value of the reference currency rises or falls, its purchasing power is affected; also, its pegged currency price is equally affected. But, when the exchange rate mechanism is fixed, the price change will not reflect in the local market as the exchange rate takes care of the fluctuations.
To maintain its fixed or nominal exchange rate, a central bank constantly continues to buy and sell its local currency as well as the reference currency. This often leads to artificial supply and demand of both currencies. When there is an increased demand for foreign exchange, the central bank can supply from its reserves at a fixed rate. Later they can buy back the local currency; creating an artificial demand thereby boosting its value.
The US dollar is the most powerful currency in the world. In our world today, over 60 countries peg their local currency to the U.S dollar. Also, about 11 countries and 5 United States territories have adopted the USD. This adoption means that the governments have given up their power to formulate an independent monetary policy and allowed the Federal Reserve (Fed) and the United States to manage the currency of their nation.
A monetary union is an agreement by two or more countries to adopt a single currency and peg it to the same reference currency. An example of an existing monetary union is the European Union (EU). Though motivated by political, social, and economic reasons, there are about 19 sovereign countries that have adopted Euro as their official currency.
Best Forex Trading Course

There is no doubt all these things may seem a bit technical to follow. In fact, the price makes so many wild swings each day that it can be very hard to measure buying pressure or selling signals. Also, learning all the technical analysis you need for forex takes more than just a day. Instead of relying on the odd article here and there, you may want to get a full detailed course to take you through all these situations.
Here is where the idea of the Asia Forex Mentor by Ezekiel Chew comes in. The course is a robust introductory guide that will give you the knowledge you need to trade forex. It’s a beginner-friendly guide as well that works for folks who want to trade forex and any other financial asset.
The Asia Forex Mentor will not just teach you how to predict price shifts, daily volume, and these other technical indicators. It will also teach you how to manage capital and explore some of the most advanced risk control measures in the world. After all, as long as you are managing your capital correctly, identifying overbought and oversold pairs will be the easier part.
Also, if you are an advanced trader looking to learn some of the tricks used by leading banks, this course is also ideal. As a matter of fact, The Asia Forex Mentor is developed by someone who has taught some of the leading investment bankers how to trade forex. You will be able to identify a losing trade, gauge price movement under immense trading pressure, and maintain a level head even when the markets are volatile.
| RECOMMENDED TRADING COURSE | REVIEW | VISIT |
|---|---|---|
 | #1 Forex, Crypto and Stocks trading course. Ranked most comprehensive by Investopedia and Best by Benzinga. Free to Try! |  |
Best Forex Brokers
| Broker | Best For | More Details |
|---|---|---|
 |
| securely through Avatrade website |
| Broker | Best For | More Details |
|---|---|---|
| securely through FXCC website |
Conclusion: Floating Exchange Rate

A floating exchange rate is a system where a country’s currency price or exchange rate is allowed to fluctuate in tandem with supply and demand as obtained from the foreign exchange market. Many nations in the world use floating exchange rate systems; this includes the major developed economies. So, all the major currencies traded in the forex market are floating currencies.
Fixed exchange rates were globally used in the past; especially from the mid-1940s to the early 1970s when the exchange rate of a currency was equated to a defined value of Gold or other currencies. It can be adjustable or hard pegged. A monetary union is when some countries decide to accept a single currency as a single means of exchange between them.
Though some nations still peg their currency price to the U.S dollar or a basket of other major currencies, it is generally difficult to correctly fix appropriate exchange values for each currency. When the exchange rate is fixed, international trade between the countries involved will be seamless because open market prices and returns on investments can be easily predicted.
The Bretton woods system was created in 1944 at the Bretton woods conference, New Hampshire, USA. The Gold standard monetary policy was adopted: it equated the value of 35 U.S dollars to one troy ounce of gold while other currencies are to convert to the US dollars. IMF and IBRD were instituted at the conference. The Bretton woods agreement came to an end in the 1970s ushering in the era of floating exchange rates.
Floating Exchange Rate FAQs
How does the floating exchange rate affect the economy?
When a government adopts floating exchange rates, it is no longer saddled with the responsibility of managing the currency price, so it can focus on other important economic problems such as unemployment, inflation, etc. There will be no need to maintain huge foreign exchange reserves to defend its domestic currency.
A country that is economically independent of its neighbors will have better macroeconomic stability with a floating exchange rate system. With cheaper exports and unrestricted access to forex, stability of the balance of payments is ensured.
What are the implications of floating rates?
When a local currency is exposed to floating exchange rates, it is directly exposed to the daily fluctuations and volatility of the global forex market. This may affect the decisions of both investors and exporters because of uncertainty in the value of their capital and investments. In a developing nation, this situation can adversely affect economic growth or slow down recovery. As a result, existing social problems like unemployment and inflation will likely worsen.
Wilbert S
Wilbert is an avid researcher and is deeply passionate about finance and health. When he's not working, he writes research and review articles by doing a thorough analysis on the products based on personal experience, user reviews and feedbacks from forums, quora, reddit, trustpilot amongst others.