Gearing Ratio: Definition, How To Calculate, Benefits, And Examples
By Wilbert S
January 10, 2024 • Fact checked by Dumb Little Man
Want to jump straight to the answer? The best Stock Brokers are Tradestation and Tradier
The #1 Stocks and Forex Trading Course is Asia Forex Mentor
There are thousands of company stocks listed and traded on various stock exchanges all over the world. Investors and speculators keep buying and selling these company stocks every weekday. The primary aim of any investor is to make profits, so, they take time to analyze the growth and profit potentials of individual company stock before deciding to invest or not.
Various financial metrics are used to analyze a stock to determine whether it has good profit potential. One of such metrics is gearing ratios which can be used to analyze if a company’s debt is a financial risk for investors if they choose to invest.
In this review, we will explain the meaning of ‘gearing ratio’ and how it relates to a company. We will find out how to know when a gearing ratio is good or bad, how to calculate it, as well as benefits and risks associated with gearing ratios. Additionally, we’ve got Ezekiel Chew; the veteran forex trader, trainer, and mentor, to share his take on gearing ratio.
What is Gearing Ratio?

The term ‘gearing ratio’ refers to the financial ratios that are used to compare debt to equity or assets. Investors, analysts, and lending institutions use these values to determine the quality of a firm’s operations and the financial risk involved when dealing with the company.
The most popular gearing ratios are debt to equity ratios, debt-to-capital ratios, and debt-service ratios. There is no industry average or general guidelines to distinguish a company with bad or good gearing ratios. But, 25% – 50% is considered an optimal gearing ratio except in cases where a company’s debt is high because it is necessary to ensure smooth operations.
Well-established companies may become highly geared when they embark on huge projects and acquire multiple debts with variable interest rates. This is not an indication that the company is in financial distress.
Gearing Ratio of a Company
A company’s gearing ratio is a metric that compares its shareholders’ equity to the total debt owed. It measures the extent to which a company is funded by creditors’ funds or money contributed by its shareholders.
The capital structure of a company is composed of debt and equity. Typically, a company’s financial operations are funded from its retained earnings, but there are times when it is insufficient especially for new projects or expansions. In such times, the company may source additional funds through debt financing or shareholders’ equity.
Debt financing is the process of raising funds by a company through debt instruments such as bank loans, corporate bonds, credit cards, etc. This form of capital does not affect company ownership but it increases the company’s short or long-term liabilities because all creditors must be repaid.
Short-term debt may be used to fund daily operations while long-term debt is used to purchase equipment, and machinery, or fund building projects. Unfortunately, the cost of debt capital is interest payments. Huge debts like a mortgage is a long-term debt but they may come with lower interest rates.
Equity financing is the raising of funds by selling shareholder equity to investors. This means selling part of the ownership of the company to the public. This is done through an initial public offering (IPO) or secondary offerings if the company is already a public company. Equity capital is not borrowed funds and no repayment is required. Even when a company is liquidated, creditors are given priority and common equity shareholders are paid last.
Good or Bad Gearing Ratio Explained

A company’s gearing ratio may be good or bad when compared with the gearing ratios of its competitors; that is, other companies in the same industry. A company with a low gearing ratio will be able to pull through in times of economic downturns because it maintains low debts and good profits.
Conversely, a company with a high gearing ratio will have huge debt levels and more debt when compared to competitors with low gearing ratios. The firm’s operations will likely be run through loans and bank overdrafts. A highly geared company is at a high risk of becoming insolvent in times of economic difficulties or when interest rates soar.
Generally, the following applies to gearing ratios:
- A high gearing ratio is above 50%
- An optimal gearing ratio is from 25-50%
- A low gearing ratio is below 25%
How to Calculate a Gearing Ratio
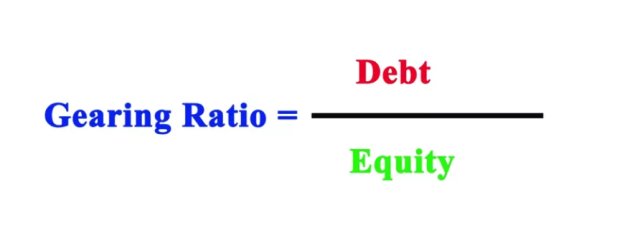
There are many gearing ratio calculations, but the most common way is to use the debt to equity ratio method. First, you will compute the company’s total debt and divide it by the total shareholders’ equity, and express it as a percentage.
Debt to equity ratio = (long term debt + short term debt + bank overdrafts)/ shareholders equity
Debt ratio = Total debts/ Total assets
Equity ratio = Total equity/ Total assets
Gearing ratio formula = any of the ratios above X 100
The shareholders’ equity is the funds contributed by the owners of the company. After calculating the required ratio, the gearing ratio is obtained by expressing it as a percentage. All data required for the calculations above can be found on the company’s balance sheet.
Gearing Ratio Example
Assuming a company has a total debt of $500,000, the balance sheet shows that the total equity owned by the shareholders is $600,000. Then we can calculate the gearing ratio using the debt to equity ratio as follows:
Debt to equity ratio = (500,000/600,000) = 0.833
Gearing ratio = (0.833 X 100) = 83.3% which is high; this means that the company is exposed to more risk if a sudden economic downturn occurs.
If company B has $10 million in total equity from stakeholders and total debt of $1.5 million. Then the debt to equity ratio will be 0.15 and the gearing ratio is 15% which is low.
Benefits of Gearing Ratios

Investors may use gearing ratios to establish a company’s financial leverage before making their decisions. Financial leverage is the use of borrowed capital to fund an investment or project with the hope that the investment will yield returns that will offset the borrowed funds. A high financial leverage ratio indicates that a company is running its operations from borrowed funds while low leverage indicates the opposite.
Lending institutions may use gearing ratios to determine whether a company is creditworthy or not. A low gearing ratio often translates to low risk while a high gearing ratio may indicate a high risk of default.
By constantly calculating its gearing ratios, a company can manage its debt levels and make efforts to reduce its debts. Some of the effective methods of reducing gearing ratios are:
- Raising money from shareholders by selling shares
- Reducing operational and overhead costs and paying off debts
- Negotiating with creditors to convert their loans to the company shares
Risks of Gearing Ratios
Well-established companies can operate with a high gearing ratio and still remain stable and viable. This is why it is necessary to compare companies that belong to the same industry before determining whether the debt ratio is high or not. Sometimes, gearing ratios are not good indicators of financial difficulties.
Gearing ratios are limited when it comes to measuring the performance and financial structure of a company. A company may be in debt but still very productive and making huge sales.
Best Stocks and Forex Trading Course

The best Forex trading course is the One Core Program from Asia Forex Mentor by Ezekiel Chew. While trading skills are lucrative, it may take you so long to grasp what works and what doesn’t. It builds your skills from the viewpoint of a new trader with fear into an advanced trader working with strategies.
Your best option is a great course. Trainers and mentors are aware of what will help you conquer the markets. Fumbling alone can waste your chance at a lifetime career in trading. A course helps you fast-track on a tried and tested model.
Many traders make a final stop at the One Core Program. Which is among the top ten credible courses you can bank on? Traders go on to hit six-figure trades following a proven model. It’s a course that has helped retail and institutional traders transform their trading careers.
| RECOMMENDED TRADING COURSE | REVIEW | VISIT |
|---|---|---|
 | #1 Forex, Crypto and Stocks trading course. Ranked most comprehensive by Investopedia and Best by Benzinga. Free to Try! |  |
Featured Investing Broker of 2024
| Broker | Best For | More Details |
|---|---|---|
 | Advanced Non US Traders Read Review | securely through Avatrade website |
 | Intermediate Non-US Traders Read Review | securely through FXCC website |
Overall Broker | securely through Forex.com website | |
 | Professional Forex Traders Read Review | securely through Interactive Brokers website |
| Broker | Best For | More Details |
|---|---|---|
 | Advanced Traders Read Review | securely through Tradestation website |
 | Intuitive Platforms Read Review | securely through Tradier website |
 | Powerful Services at a Low Cost | securely through Tradezero website |
 | Professional Forex Traders Read Review | securely through Interactive Brokers website |
Conclusion: Gearing Ratio

Gearing ratios measure the capital or equity of a company in comparison with the debts it owes. A low gearing ratio indicates a financially sufficient company while a high ratio means more debts than shareholder equities.
One of the popular methods used for calculating the gearing ratio is to add all the debts of the company, divide it by the total equity from shareholders and express the result as a percentage. A gearing ratio less than 25% is low, 25-50% is optimal, and above 50% is high.
Investors consider gearing ratios when making investment decisions for companies within the same industry. By comparing their operations and equity ratios, they may estimate the risks involved in buying the stocks of companies. Credit institutions also use it to estimate the risk of default before making decisions.
One core program is a unique forex and CFD trading course created by the celebrated forex expert; Ezekiel Chew. The program teaches his proprietary trading strategy that has been tested and proven as it has transformed many newbies into successful forex traders. You can enroll for the course via the Asia Forex Mentor website.
Gearing Ratio FAQs
What is a good gearing ratio?
A good gearing ratio for a well-established company probably operating in a regulated industry should be between 25% – 50%. Generally, a gearing ratio below 25% is good because that is the range regarded by credit institutions, lenders, and investors as low risk.
Is the gearing ratio and Debt ratio the same?
No, they are not the same. Debt ratios are calculated as the total debts divided by the total assets. A gearing ratio is a set of ratios that includes some of the following:
- Debt to equity ratio
- Debt ratio
- Equity ratio
- Debt to capital
Wilbert S
Wilbert is an avid researcher and is deeply passionate about finance and health. When he's not working, he writes research and review articles by doing a thorough analysis on the products based on personal experience, user reviews and feedbacks from forums, quora, reddit, trustpilot amongst others.